Butterfly valves are indispensable components in various industries. They serve critical roles in regulating fluid flow. Their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of operation make them popular choices. Selecting the appropriate butterfly valve entails considering several factors. This is to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This guide explores the intricacies of choosing the suitable butterfly valve. It covers essential considerations, types, materials, and applications.
Before going into the selection process, it’s crucial to know the fundamentals. Unlike traditional globe or gate valves, butterfly valves control flow using a disc. It pivots perpendicular to the flow direction. When the disc is parallel to the flow, it allows full passage. When positioned vertically, total flow is blocked. This mechanism enables quick operation and efficient flow control. This makes them ideal for applications requiring fast shutoff or modulation.
Types of Butterfly Valves
Concentric Butterfly Valve
It features a symmetrical design with the shaft positioned at the center of the disc. This design facilitates uniform sealing, making it suitable for general-purpose applications.
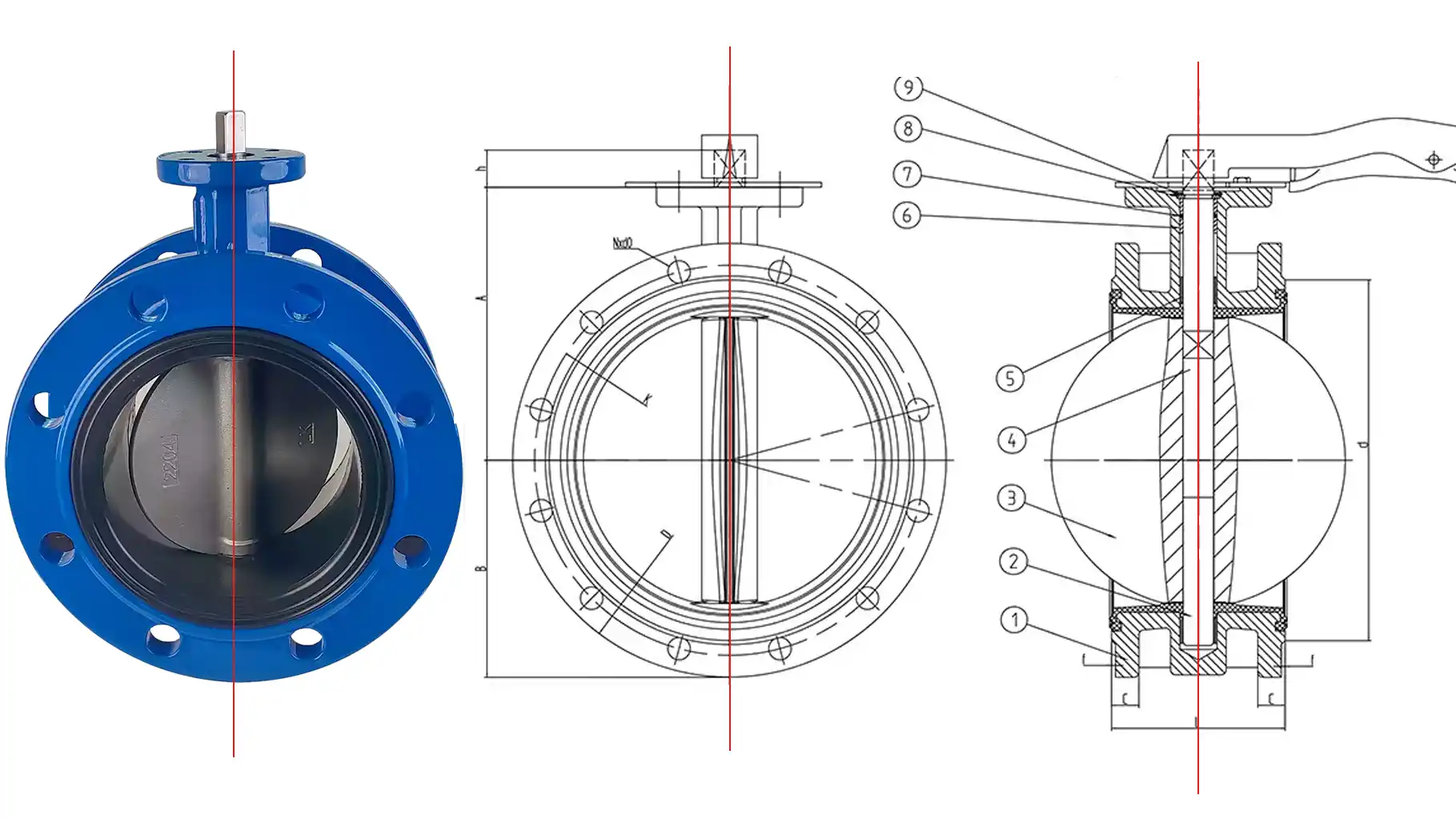
Double Offset Butterfly Valve
Double offset butterfly valves incorporate an offset shaft and disc geometry to improve sealing performance and reduce friction during operation. They offer enhanced sealing capabilities and are ideal for high-pressure or high-temperature applications.
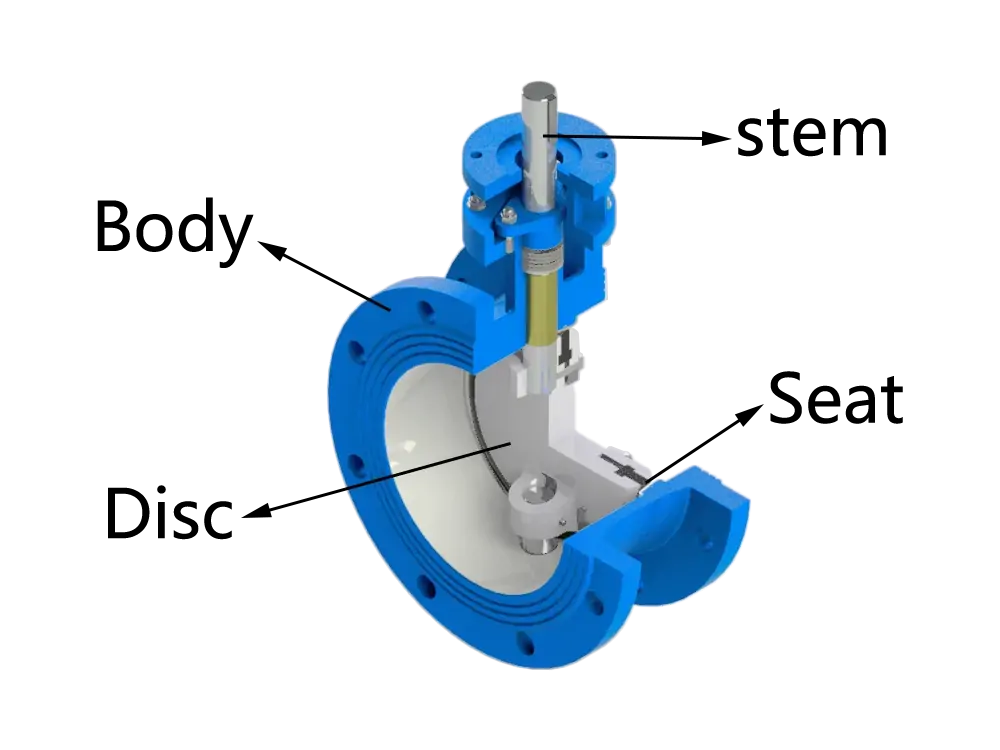
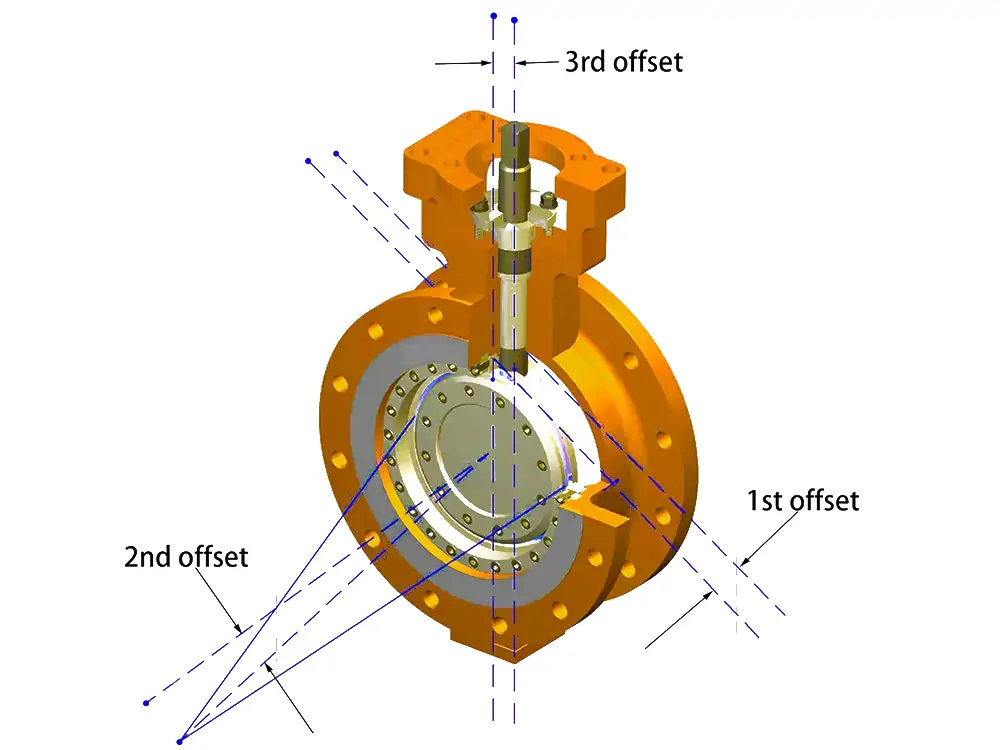
Triple Offset Butterfly Valve
Utilizes an eccentric shaft and triple-offset disc geometry to achieve bubble-tight sealing. It offers minimal friction. Triple offset butterfly valves excel in demanding applications. Prefer it if you need tight shutoff and resistance to wear and erosion.
Selecting the Right Butterfly Valve for Your Application
Selecting the right butterfly valve involves a thorough analysis. Let’s delve into these aspects:
Application Requirements
Understanding the application’s specific demands is paramount. Factors such as flow rate, pressure, and temperature are important. Media type and required shutoff capabilities are also essential. Different applications may need varying degrees of flow. Control precision and resistance to corrosion or abrasion are also vital.
Valve Size and Pressure Rating
Matching the valve size to the pipeline is essential. This is to ensure seamless integration and adequate flow capacity. Selecting a valve with the appropriate pressure rating is crucial. Pressure ratings should align with the system’s operating pressure. This ensures safety and reliability.
Operating Mechanism
You can operate butterfly valves manually, pneumatically, or electronically. The choice of operating mechanism depends on various factors. Frequency of operation, accessibility, and automation requirements are essential. Applications requiring frequent adjustments may enjoy automated ones. This is for its enhanced control and efficiency.
Valve Types
Butterfly valves come in various types, each designed to meet specific application requirements.
- Wafer: Compact design suitable for space-constrained installations.
- Lug: Features threaded inserts for easy installation and removal without disrupting the pipeline.
- Flanged: Bolted to the pipeline using flanges, offering secure connections and easy maintenance.
- High-Performance: Engineered for demanding applications with enhanced durability and sealing capabilities.
Factors to Consider When Choosing the Butterfly Valve

1. Material Selection
The choice of materials is essential. They impact its performance and longevity. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and various alloys. Below are the parameters you need to look at:
| General Applications: |
|
| Corrosion-Resistant Media: |
|
| High-Temperature Applications: | High-temperature alloys (e.g., Inconel, Incoloy) |
| Low-Temperature Applications: | Low-temperature carbon steel |
| Chemically Corrosive Media: |
|
-
Fluid Compatibility
Consider the type of fluid the valve will be handling. Different materials have varying resistance to corrosion and chemical attack. For corrosive fluids like acids, select corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys. Materials like ductile iron or PVC may suffice for less aggressive fluids.
-
Temperature Range
Test the temperature range of the application. Some materials, such as certain plastics, may have limited temperature tolerances. Metals like stainless steel or carbon steel can withstand higher temperatures. Ensure the selected material can handle the anticipated temperature fluctuations without compromising performance.
-
Pressure Rating
Consider the pressure rating required for your application. Materials like carbon steel and stainless steel are popular for their high-pressure capabilities. This makes them suitable for applications with elevated pressure requirements. Plastic materials may have lower pressure ratings. They can still be suitable for low-pressure applications.
-
Abrasion Resistance
Choose a material with good abrasion resistance. Hardened materials like stainless steel are ideal for such applications.
-
Hygienic Requirements
Hygiene is paramount in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, or biotechnology. Choose materials that are easy to clean and sterilize. Use stainless steel or certain polymers approved for food contact.
-
Environmental Factors
Consider environmental factors. Outdoor exposure, UV radiation, or atmospheric conditions are some of them. Materials like PVC or CPVC may degrade when exposed to sunlight over time. Metals like stainless steel or bronze are more resistant to environmental degradation.
-
Cost Considerations
Cost is a significant factor. Balance the material selection with your budget constraints. In some cases, a more expensive material may provide long-term cost savings. This is due to reduced maintenance or replacement frequency.
It’s important to note that each material has its advantages and limitations. Therefore, when selecting the material for the valve body and seat of butterfly valves, it’s crucial to consider the media’s properties, operating conditions, material availability, and cost. Consulting with professional engineers or valve manufacturers is recommended in specific applications to obtain more accurate advice.
2. Sealing Mechanism
The sealing mechanism plays a critical role in preventing leakage. It ensures reliable operation. Below mentioned are the various sealing mechanisms you can choose from:
-
Rubber Seals (Elastomer)
Butterfly valves use elastomeric seals. EPDM, NBR (Buna-N), Viton, or silicone are good choices. These seals offer excellent resilience and flexibility. They provide a tight seal even against moderate pressures. EPDM is popular for its compatibility with water, steam, and various chemicals. NBR offers resistance to oils and hydrocarbons. Prefer Viton for applications requiring resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. Silicone seals are suitable for sanitary applications due to their hygienic properties.
-
PTFE (Teflon) Seals
PTFE seals are popular for their exceptional chemical resistance. They have low frictional properties. They provide a tight seal even in high-temperature and corrosive environments. PTFE-lined butterfly valves are good for chemical processing. People also use them in the pharmaceutical and food industries. This is where aggressive chemicals or sanitary conditions are present.
-
Metal Seals
Metal-seated valves use metal-to-metal contact between the disc and seat for sealing. They offer superior durability and resistance to high temperatures. Compared to elastomeric seals, they are good for abrasion and pressure differentials. However, they need higher operating torque and are prone to seat wear over time.
-
Triple Offset Design Seals
Triple-offset butterfly valves feature a unique sealing mechanism. Here, the disc rotates with three different offsets (conical, eccentric, and inclined) to achieve a tight shutoff. This design minimizes wear on the sealing surfaces, improving sealing performance. Prefer triple-offset valves in high-pressure, high-temperature applications. They are good for oil and gas, refining, and power generation industries.
-
Resilient VS High-Performance Seals
Resilient seals provide excellent sealing performance. They also work well under moderate pressures and temperatures. High-performance seals offer superior performance in demanding conditions such as high temperatures. They are good for abrasive media or vacuum applications.
Operating Conditions:
Check the operating conditions, including temperature, pressure, and media characteristics. Cycling frequency is also important to determine the most suitable sealing mechanism. Ensure the selected seal material can withstand your application without compromising performance.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with standards and regulations ensures reliability, safety, and interoperability. Within the system, it also mitigates potential risks associated with non-compliance. So, please ensure that you follow the following requirements:
-
Understand Industry Standards
Familiarize yourself with industry-specific standards. Industries have standards that govern valve performance, materials, and safety requirements. These include oil and gas, water treatment, food and beverage, etc.
-
Certifications and Approvals
Look for butterfly valves that carry relevant certifications and approvals. They are from recognized regulatory bodies and standards organizations. Common certifications include ISO, API, ANSI, ASTM, ASME, NSF, and FDA. Others depend on the industry and application requirements.
-
Safety Standards
Consider safety standards and guidelines relevant to your industry. For process safety, follow those outlined by organizations like OSHA or SIL. This is for industries like oil and gas or chemical processing. Select butterfly valves that meet or exceed these safety standards. This helps mitigate risks and ensure safe operation.
-
Installation and Maintenance Guidelines
Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure compliance with installation and maintenance. Proper installation and maintenance help prevent issues such as leaks and valve failures.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right butterfly valve requires careful consideration of application requirements. Consider operating conditions, valve types, materials, and compliance standards. By understanding these factors, you can select the appropriate valve. Consultation with industry experts and valve manufacturers can further help the selection process.




