Classification of Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves serve many applications due to their efficient 1/4 turn design and versatility. Butterfly valves are used to start and stop the flow of fluid through a pipeline, and sometimes to regulate flow. Compared to other valves such as gate valves, stop valves, etc., butterfly valves are known for their fast operation, compact design, and low price. In this article, we analyze the most frequently asked questions by customers, that is the classification of butterfly valves.
Question 1: What are the three types of butterfly valves?
The classification of butterfly valves is according to their installation configuration. The three main types are: wafer type, flange type, lug type.
-
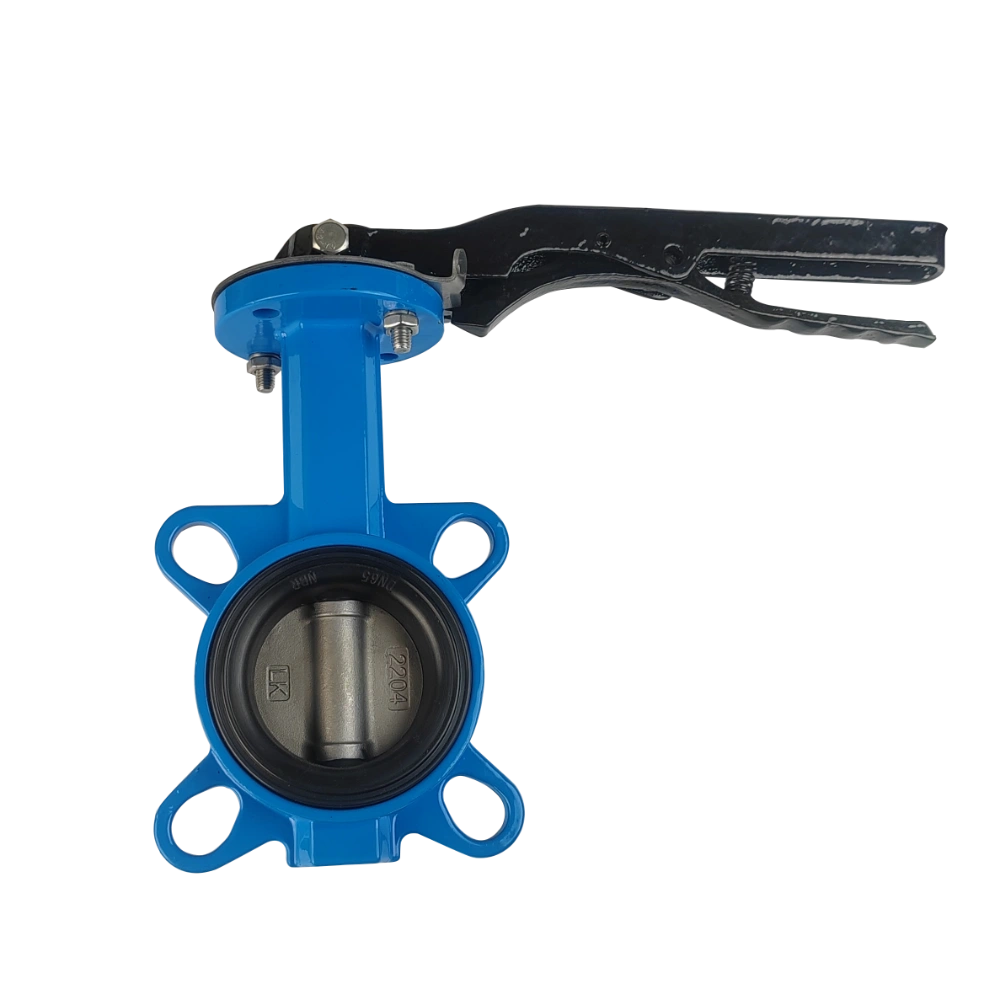
Wafer butterfly valve
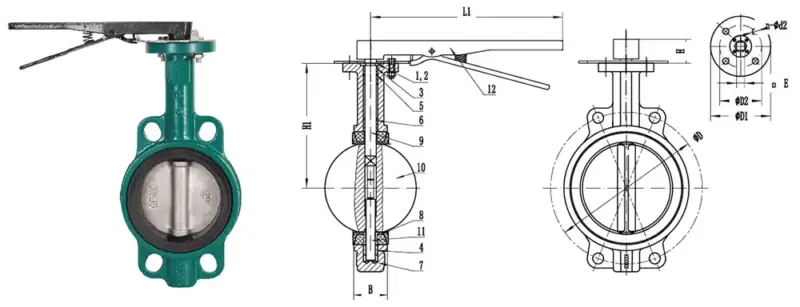
Wafer butterfly valve is one of the most common and economical types of small and medium-sized butterfly valves. It only requires 4 bolts to clamp between the two flanges of the pipeline.
Advantages:
– Cost-effective, small butterfly valves can meet the control of fluids in pipelines.
– Easy to install and disassemble, only 4 bolts are required to install and disassemble. So it can be applied to scenes that require frequent disassembly.
– Suitable for multiple standards, PN6/PN10/PN16, CL150, JIS5K/10K.
– Lightweight, short structure length, suitable for environments with small space.
Disadvantages:
– Not suitable for medium and high pressure applications. .
– Cannot be used as a pipeline end valve. Once only one end of the flange is left, the wafer butterfly valve will fall off.
– There are only 4 ears on the valve body and no bolt holes, so it is not as strong as flanges and lugs.
Application:
– Water treatment: This is the most basic application of butterfly valves.
– HVAC: Regulate, heat and cool air flow in HVAC systems.
– Food and beverage processing: Food-grade butterfly valves can be used for the flow of liquids in food and beverage processing.
-
Flange butterfly valve
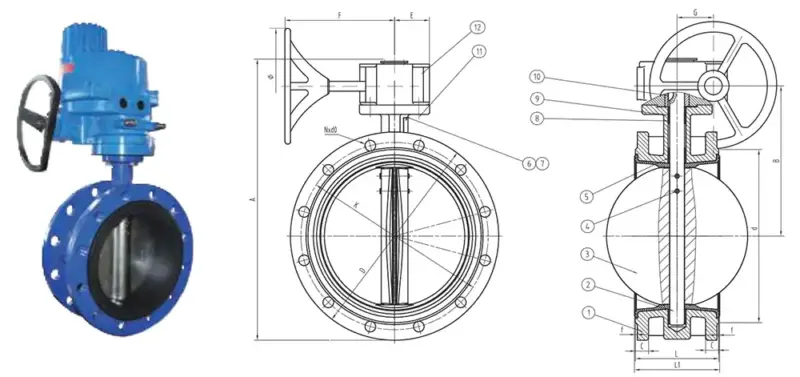
Flange butterfly valve, with 2 integral flanges at both ends of the valve body, can be directly fixed to the pipe flange with 2 sets of stud bolts.
Advantages:
– More durable than wafer type.
– a variety of seat materials can be equipped with, including rubber, PTFE and other elastic seats. These are for low temperature and low pressure liquid processing. You can also equip it with metal seats. They can handle low, medium, and high temperatures, pressures, and flow rates.
– the double flanged type Can be used for larger diameter pipes, up to DN3000.
– Can be used at the end of the pipe.
Disadvantages:
– Heavy weight, high production cost.
– More complicated to install and remove, so the process takes longer.
– Usually use worm gear, electric, pneumatic and other actuators, occupy more space and cost more.
Application:
Soft seal butterfly valve is used in the same wafer, but different is metal seal butterfly valve.
– Oil and gas.
– Chemical processing: can handle corrosive chemicals.
– Power generation: used in steam and cooling systems.
-
Lug butterfly valve
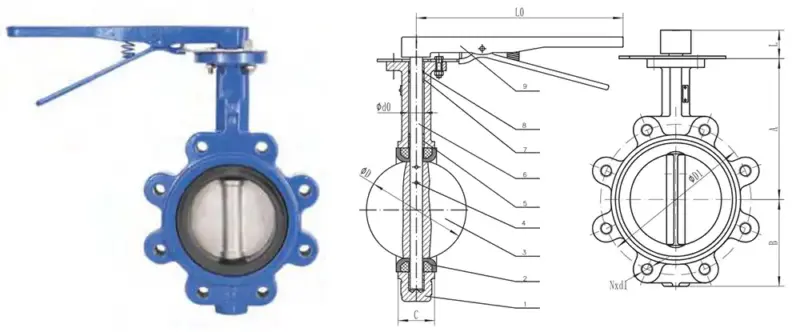
Lug butterfly valve is similar to the wafer butterfly valve, with the same structural length, but there are threaded lugs on both sides of the valve body. Long bolts need to be screwed into these ears to connect with the flange of the pipe. They strike a balance between wafer and flange in terms of cost and performance.
Advantages:
– Suitable for the end of the pipe, the downstream side can be disassembled without affecting the upstream pressure.
– Stronger connection compared to the wafer type. Why? Don’t forget the lug butterfly valve, which also has threaded ears with fixing capabilities.
Disadvantages:
– Because of the extra thick small ears, it is heavier and more expensive than the wafer type.
– For low and medium pressure applications, although it is stronger than the wafer butterfly valve, it is still not as good as the flange type.
Applications:
– Fire protection system: often used in fire sprinkler systems where isolation of parts may be required.
– Municipal water supply system: Due to its strength and flexibility, it is suitable for pipes that need to be cleaned many times.
Question 2: What are the two general types of butterfly valves?
This classification of butterfly valves is named according to the design of its internal components (valve disc and valve seat). The two general types are: concentric type, eccentric type.
-
Concentric butterfly valve
Also known as zero eccentric or soft seat butterfly valve. The valve stem passes through the center line of the valve disc and the center line of the valve body. There is no eccentricity.
Advantages:
– Simple design and low price.
– Small torque for opening and closing.
– Suitable for common applications such as low-pressure and low-temperature water treatment.
Disadvantages:
– The valve seat is a soft elastic seal, such as rubber and PTFE, so the pressure and temperature cannot be too high.
– It is not available with hard particles or strong corrosive media.
– The wear and aging of the elastic valve seat cannot stand the test of time.
Applications:
-Municipal water supply system
-Food and beverage
-HVAC
-
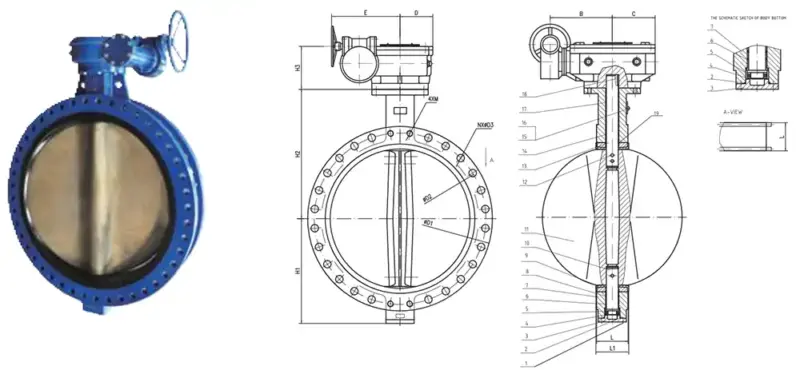
Eccentric butterfly valve
Eccentric butterfly valves include double eccentric and triple eccentric designs.
Double eccentricity: The valve stem deviates from the center line of the disc and the body. It is to reduce friction during operation.
Triple eccentricity: On the basis of double eccentricity, the sealing surface of triple offset type is also eccentrically, and the sealing surface is conical. The purpose is to keep the disc away from the seat during operation, thereby minimizing wear. Usually, the sealing surface of the triple eccentricity adopts metal sealing.
Advantages:
– Suitable for higher pressure and temperature applications.
– Reduce friction and wear, and extend service life.
– Enhanced sealing performance.
Disadvantages:
– Compared with the concentric type, the production and installation of eccentric butterfly valves are more complicated and expensive.
– Requires precise manufacturing and assembly to ensure its sealing performance.
Applications:
– Petrochemical industry: Used in refining and processing due to its ability to handle high pressure and high temperature.
– Power plants.
– Marine and offshore services.




